Support hardware-aware affinity for pods on k8s cluster¶
https://blueprints.launchpad.net/tacker/+spec/hardware-aware-pod-affinity
Problem description¶
In case of deploying a Container Network Function on the VNF of a Kubernetes cluster with the blueprint “CNF Support with ETSI NFV specifications” [1], the Pods may be scheduled on the same physical Compute server while they are labeled with anti-affinity rules [2]. The anti-affinity Rule can deploy the Pods on different worker nodes, but the worker nodes may be in the same server. In this spec, we propose a hardware-aware affinity for Pods.
Proposed change¶
This spec proposes the design for pod deployment operations with hardware-aware affinity. It is assumed that a label is given when the Worker-node is deployed as the VNF-A process, and based on this label, the Worker-node to which the pod is deployed is determined in the VNF-B process. The following changes are required.
VNF-A: Create a VM, set up the Kubernetes cluster and set labels to Worker-node.
MgmtDriver sets
labelbased on which compute server the new created Worker-node have been deployed on by invoking a shell script ininstantiate_endof instantiation process for VNF-A
In addition, this specification assumes that each Worker-node is deployed to a different compute server, and this can be done using the anti-affinity mechanism. However, it is not supported to deploy a VM with anti-affinity settings in TOSCA file because this parameter is not supported by Heat-translator while TOSCA v1.2 has definition. Therefore, the following modifications are required.
Heat-translator translates the anti-affinity settings defined in the TOSCA file into the Heat template.
VnflcmDriver deploys the Worker-node on a different compute server based on the anti-affinity settings specified in the Heat template.
Note
On the other hand, using the UserData method of instantiation with BaseHOT described in the spec of LCM-operation-with-user-data, there is no need to change the existing Tacker implementation.
VNF-B: Deploy CNF on the Kubernetes cluster inside VNF-A and VNFC(Pod) is created on the Worker-node selected by label.
There is no need to change the existing Tacker implementation for VNF-B. Instantiate operation for CNF is same as described in the spec of CNF-with-VNFM-and-CISM. Note that the Kubernetes object file must contain definitions for anti-affinity mechanism to meet this specification of pod deployment operations with hardware-aware affinity.
Note
Kubernetes v1.16.0 and Kubernetes python client v11.0 are supported for Kubernetes VIM.
VNF-A: Create a VM, set up the Kubernetes cluster and set labels¶
Basically, the specification is based on mgmt-driver-for-k8s-cluster. As an additional change, we suggest an operation to deploy a pod that supports hardware-aware affinity by labeling the Worker-node.
The diagram below shows assigning a label to Worker-nodes newly created:
+-----------+ +-----------+ +---------+ +--------+
| Heat | | LCM | | Cluster | | |
| Template | | operation | | Install | | VNFD |
| (BaseHOT) | | UserData | | Script | | |
+-----+-----+ +-----+-----+ +-------+-+ +-+------+
| | | |
| | v v +---------------+
| | +----------+ | Instantiation |
| +----------->| | | Request with |
| | CSAR | | Additional |
-------------------------->| | | Params |
+----+-----+ +--------+------+
| |
+----------+ |
| |
| |1.Instantiate
| | VNF
+--+--------+------------+
| v v |
+-------------------+ | +------------------+ |
| | | | Tacker-server | |
| +-----+ | | +------------------+ |
| | Pod | | | | |
| +-----+ | | +----------+ |
| |<----+ | +------------------+ | |
| Kubernetes | | +------------+ | | +--------------+ | | |
| cluster(Worker02) |<-+ | | Kubernetes | | | | Kubernetes | | | |
+-------------------+ | | | cluster | | | | InfraDriver | | | |
+-------------------+ | | | (Master) |<--+ | | | | | | |
| Compute02 | | | +------------+ | | | +--------------+ | | |
+-------------------+ | | 3.Setup new | | | | | |
| | Worker-node | | | +-------------+ | | |
| | and set label | | | | MgmtDriver | | | |
+-------------------+ | | during k8s cluster | | | +-----+-------+ | | |
| | | | installation | | | | |<+ |
| +-----+ |<-|--+----------------------+--+-+--------+ | |
| | Pod | | | | | | +-------------+ | |
| +-----+ | | | | | |OpenStack | | |
| |<-+ | | | |InfraDriver | | |
| Kubernetes | | | | | +-----+-------+ | |
| cluster(Worker01) | | 2. Create VMs | | | | | |
+-------------------+ +-------------------------+--+-+--------+ | |
+-------------------+ | | Tacker conductor | |
| Compute01 | | +------------------+ |
+-------------------+ +------------------------+
The diagram shows related component of this spec proposal and an overview of the following processing:
Tacker-server receives instantiation requests for VNF by user.
OpenStackInfraDriver creates new VMs when building the initial Kubernetes cluster.
MgmtDriver setups new Worker-node on new VMs and sets
labelbased on which compute server the new created Worker-node have been deployed on by invoking a shell script. These processes are same as described in the specification of mgmt-driver-for-k8s-cluster, except for the process of settinglabel.
Note
Using Kubernetes AntiAffinity mechanisms can meet the requirements of
this specification. Worker-nodes can be labeled using some types of
Topology Keys: hostname, zone, and so on. When, for example,
the hostname is referred to, a specific node can be selected from
among a plurality of worker-nodes. Based on this label, the node on
which the pod is to be deployed can be determined by the logic of
AntiAffinity. However, the specification requires that you control
which compute server the pod is deployed to on which node, so you
need to use the topology key of zone.
Note
The diagram above assumes that the newly generated Worker-node is
labeled based on the hostname of hardware server for the topology
key of zone.
If Worker-node was created in Computer01, it is labeled as follows:
kubernetes.io/zone=Compute01
If Worker-node was created in Computer02, it is labeled as follows:
kubernetes.io/zone=Compute02
Required components of CSAR package for Instantiation¶
This spec is assumed to be satisfied in two ways. One is the UserData method, which requires defining the relevant settings in the BaseHOT, and the other is the TOSCA method specified in SOL 001.
BaseHOT: This UserData method does not require any Tacker implementation changes. The BaseHOT requires the configuration of an
srvgroupthat contains policy definitions for the anti-affinity.TOSCA: This method requires new support for the
AntiAffinityRuleandPlacementGroupparameters in the translation process of “HeatTranslator”.
VNFD & BaseHOT definition
VNFD
VNFD is same as described in the “VNFD for Kube-adm with TOSCA template” chapter of spec mgmt-driver-for-k8s-cluster.
Heat template
You need to define
srvgroupas shown in the sample below.parameters: ... srvgroup_name: type: string description: Name of the ServerGroup default: ServerGroup resources: srvgroup: type: OS::Nova::ServerGroup properties: name: { get_param: srvgroup_name } policies: [ 'anti-affinity' ] masterNode: type: OS::Heat::AutoScalingGroup properties: desired_capacity: 3 max_size: 5 min_size: 3 ... scheduler_hints: group: { get_resource: srvgroup } workerNode: type: OS::Heat::AutoScalingGroup properties: desired_capacity: 3 max_size: 5 min_size: 3 ... scheduler_hints: group: { get_resource: srvgroup }
VNFD with TOSCA template
It is basically the same as described in the “VNFD for Kube-adm with TOSCA template” chapter of spec mgmt-driver-for-k8s-cluster, but you need to add the following settings.
min_number_of_instancesof thetargetsmust be set to 2 or higher.You need to add
PlacementGroupandAntiAffinityRule.
node_template: ... masterNode: type: tosca.nodes.nfv.Vdu.Compute ... workerNode: type: tosca.nodes.nfv.Vdu.Compute properties: name: workerNode description: workerNode vdu_profile: max_number_of_instances: 5 min_number_of_instances: 3 groups: antiAffinityGroup: type: tosca.groups.nfv.PlacementGroup members: [ masterNode, workerNode ] policies: policy_antiaffinity_group: type: tosca.policies.nfv.AntiAffinityRule targets: [ antiAffinityGroup ] properties: scope: nfvi_node scaling_aspects: type: tosca.policies.nfv.ScalingAspects properties: aspects: worker_instance: name: worker_instance_aspect description: worker_instance scaling aspect max_scale_level: 2 step_deltas: - delta_1 masterNode_initial_delta: type: tosca.policies.nfv.VduInitialDelta properties: initial_delta: number_of_instances: 1 targets: [ masterNode ] masterNode_scaling_aspect_deltas: type: tosca.policies.nfv.VduScalingAspectDeltas properties: aspect: worker_instance deltas: delta_1: number_of_instances: 1 targets: [ workerNode ] workerNode_initial_delta: type: tosca.policies.nfv.VduInitialDelta properties: initial_delta: number_of_instances: 1 targets: [ workerNode ] workerNode_scaling_aspect_deltas: type: tosca.policies.nfv.VduScalingAspectDeltas properties: aspect: worker_instance deltas: delta_1: number_of_instances: 1 targets: [ workerNode ]
Request data(BaseHOT/TOSCA)¶
BaseHOT
Below is a sample of body provided in the VNF instantiation request POST /vnflcm/v1/vnf_instances/{vnfInstanceId}/instantiate:
{ "flavourId": "cluster_install", "additionalParams": { "lcm-operation-user-data": "UserData/base_user_data.py", "lcm-operation-user-data-class": "BaseUserData", "input_params":"" }, "vimConnectionInfo": [ { "id": "8a3adb69-0784-43c7-833e-aab0b6ab4470", "vimId": "7dc3c839-bf15-45ac-8dff-fc5b95c2940e", "vimType": "openstack" } ] }
TOSCA
Below is a sample of body provided in the VNF instantiation request POST /vnflcm/v1/vnf_instances/{vnfInstanceId}/instantiate
{ "flavourId": "cluster_install", "additionalParams": { "input_params":"" }, "vimConnectionInfo": [ { "id": "8a3adb69-0784-43c7-833e-aab0b6ab4470", "vimId": "7dc3c839-bf15-45ac-8dff-fc5b95c2940e", "vimType": "openstack" } ] }
Following sequence diagram describes the components involved and the flow of
instantiate VNF operation in which new Worker-node is set label of zone:
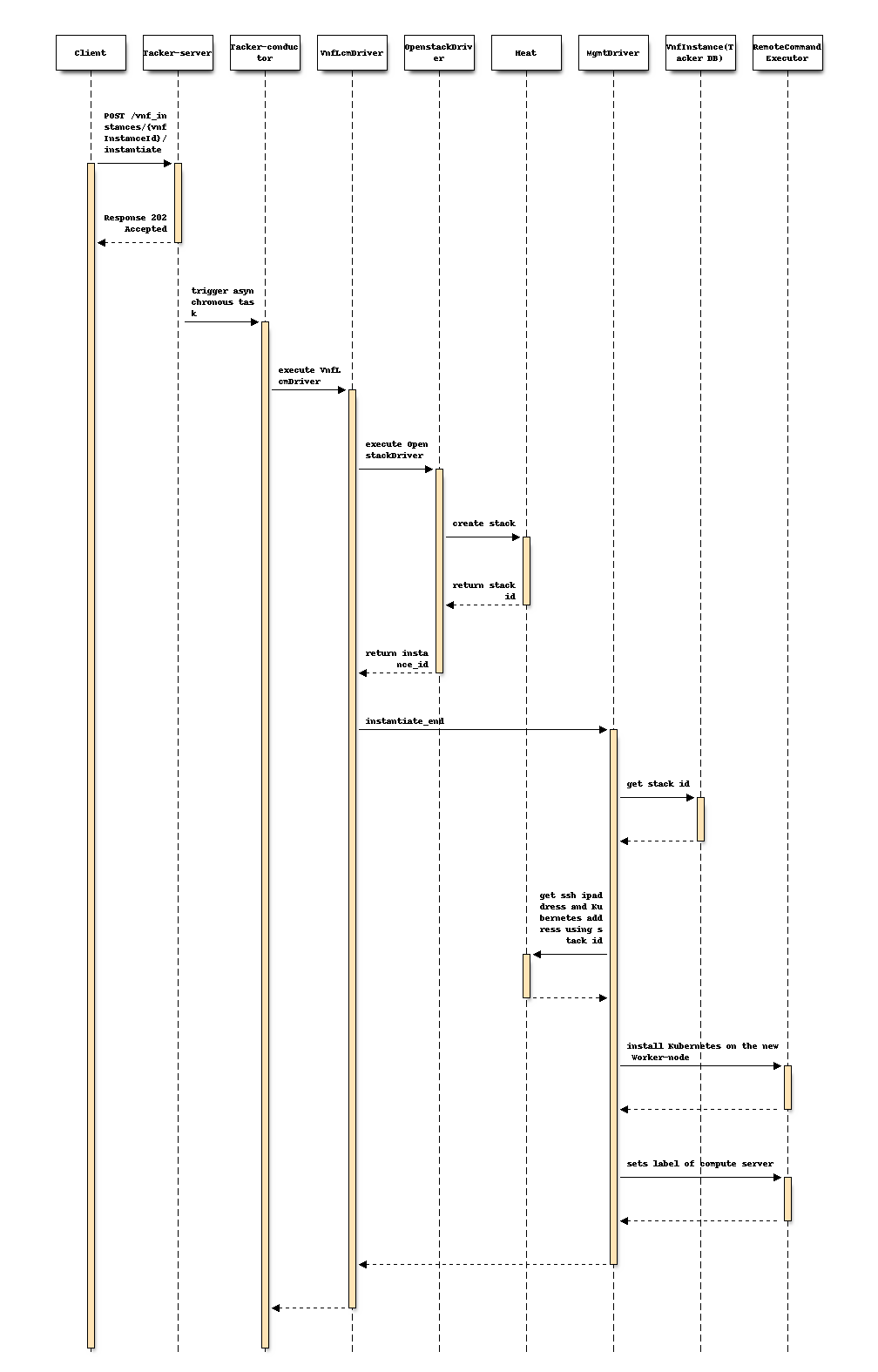
The procedure consists of the following steps as illustrated in above sequence.
Client sends “instantiate” as a POST request.
Basically the same sequence as described in the “2) Flow of Instantiation of a VNF instance” chapter of spec etsi-nfv-sol-rest-api-for-VNF-deployment, except for the MgmtDriver.
The following processes are performed in
instantiate_end.MgmtDriver gets new VM information from Heat.
MgmtDriver installs Kubernetes on the new Worker-node by a shell script as described in the spec of mgmt-driver-for-k8s-cluster
Note
The Master-node installation process is omitted here for the sake of simplicity.
MgmtDriver sets
labelbased on which compute server the new created Worker-node have been deployed on by invoking a shell script.
Note
The process of this label setting needs to be added to
scale_end and heal_end as well. Please refer to the
specification of mgmt-driver-for-k8s-scale and
mgmt-driver-for-k8s-heal for details.
Note
This sequence is described on the premise of using BaseHOT.
In case of using TOSCA method, the translation process of
“HeatTranslator” need to be modified as described in
“2) Flow of Instantiation of a VNF instance “ chapter of the spec
etsi-nfv-sol-rest-api-for-VNF-deployment, regarding new support for
the AntiAffinityRule and PlacementGroup parameter.
VNF-B: Deploy CNF on the Kubernetes cluster inside VNF-A¶
Basically, the specification is based on CNF-with-VNFM-and-CISM. On which Worker-nodes pod are generated is determined based on the label.
The diagram below shows that the pod is deployed in place based on the label assigned to the Worker-node.
+-----------+ +-----------+ +---------+ +--------+
| Heat | | LCM | | Cluster | | |
| Template | | operation | | Install | | VNFD |
| (BaseHOT )| | UserData | | Script | | |
+-----+-----+ +-----+-----+ +-------+-+ +-+------+
| | | |
| | v v +---------------+
| | +----------+ | Instantiation |
| +----------->| | | Request with |
| | CSAR | | Additional |
-------------------------->| | | Params |
+----+-----+ +--+------------+
| | 1.Instantiate
+----------+ | CNF
| |
| |
| |
+--+--+------------------+
2.Instantiate | v v |
+-------------------+ VNFC(Pod) | +------------------+ |
| | on the Worker-node | | Tacker-server | |
| +-----+ | selected by label | +---+--------------+ |
| | Pod |<----------+--------+ | | |
| +-----+ | | | v |
| | | | +------------------+ |
| Kubernetes | | +------------+ | | +--------------+ | |
| cluster(Worker02) | | | Kubernetes | | | | Kubernetes | | |
+-------------------+ +--+ cluster |------+-+-| InfraDriver | | |
+-------------------+ | (Master) | | | | | | |
| Compute02 | +------------+ | | +--------------+ | |
+-------------------+ | | | |
| | +-------------+ | |
| | | Mgmt Driver | | |
+-------------------+ | | +-------------+ | |
| | | | | |
| +-----+ | | | | |
| | Pod | | | | +-------------+ | |
| +-----+ | | | |OpenStack | | |
| | | | |Infra Driver | | |
| Kubernetes | | | +-------------+ | |
| cluster(Worker01) | | | | |
+-------------------+ | | | |
+-------------------+ | | Tacker conductor | |
| Compute01 | | +------------------+ |
+-------------------+ +------------------------+
The diagram shows related component of this spec proposal and an overview of the following processing:
Tacker-server receives instantiation requests for CNF by user.
KubernetesInfraDriver calls Kubernetes client API for instantiation, and then Kubernetes cluster instantiates pods on Worker-nodes in the specified computer server.
VNFD - Kubernetes object file¶
Kubernetes object file needs to have affinity definition as the following
sample:
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: redis-cache
spec:
selector:
matchLabels:
app: store
replicas: 2
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: store
spec:
affinity:
podAntiAffinity:
requiredDuringSchedulingIgnoredDuringExecution:
- labelSelector:
matchExpressions:
- key: app
operator: In
values:
- store
topologyKey: kubernetes.io/zone
containers:
- name: redis-server
image: redis:3.2-alpine
Note
The above is a sample configuration for deploying a new pod on a Worker-node using podAntiAffinity across a zone, here meaning compute server. It should be noted that the parameter of requirdedDirectionSchedulingIgnoredDuringExecution is a parameter representing a condition that if there is no deployment location that satisfies this condition, the pod deployment is not executed. On the other hand, if preferredDuringSchedulingIgnoredDuringExecution is specified, the pod is deployed.
Request data and sequence for instantiate CNF operation is same as described in the spec of CNF-with-VNFM-and-CISM.
Alternatives¶
None
Data model impact¶
None
REST API impact¶
None
Security impact¶
None
Notifications impact¶
None
Other end user impact¶
None
Performance Impact¶
None
Other deployer impact¶
None
Developer impact¶
None
Implementation¶
Assignee(s)¶
- Primary assignee:
Yoshito Ito <yoshito.itou.dr@hco.ntt.co.jp>
- Other contributors:
Shotaro Banno <banno.shotaro@fujitsu.com>
LiangLu <lu.liang@fujitsu.com>
Ayumu Ueha <ueha.ayumu@fujitsu.com>
Work Items¶
MgmtDriver will be modified to implement:
Identify on which computer server the new worker-node was deployed in
instantiate_end,scale_endandheal_end.Provide a sample script to be executed by MgmtDriver to set the zone label on the worker node using the compute server information.
Either of the following changes is required depending on the method:
BaseHOT: This UserData method does not require any Tacker implementation changes. The BaseHOT requires the configuration of an
srvgroupthat contains policy definitions for the anti-affinity.TOSCA: This method requires new support for the
AntiAffinityRuleandPlacementGroupparameters in the translation process of “HeatTranslator”.
Add new unit and functional tests.
Dependencies¶
The instantiate_end referenced in the “Proposed Changes” is the same as the
spec of mgmt-driver-for-k8s-cluster.
Testing¶
Unit and functional tests will be added to cover cases required in the spec.
Documentation Impact¶
Complete user guide will be added to explain the deploying operation for pod with hardware-aware affinity from the perspective of VNF LCM APIs.
