MgmtDriver with Kubernetes cluster management OSS¶
https://blueprints.launchpad.net/tacker/+spec/k8s-mgmtdriver-kubespray
This spec proposes Ansible interface for MgmtDriver to manage Kubernetes cluster VNF. As sample implementation, Tacker provides kubespray [1] as Ansible playbooks in MgmtDriver to install and configure Kubernetes cluster VNF. Also, Load Balancer to expose CNF on the Kubernetes cluster VNF will be supported.
Problem description¶
As described in specs [2] [3] [4],
Users can manage their Kubernetes cluster VNF with VNF Lifecycle Management
operations in ETSI NFV-SOL003 v2.6.1 [5].
In those specs, MgmtDriver is responsible for preamble and postamble actions
before/after the main operations.
MgmtDriver enables Users to execute any configuration logics in
<operation>_start() or <operation>_end() method.
Also, those methods support to execute shell scripts in each VM deployed in
the VNF Lifecycle Management operations.
On the other hand, Cloud Native Computing Foundation (CNCF) [6] hosts some solutions for Kubernetes cluster management. In this spec, new MgmtDriver supports kubespray [1] as sample of Ansible playbook.
The following new features will be supported:
Kubernetes cluster management with kubespray Ansible playbook.
VNF Lifecycle Management for Load Balancer to expose CNF on Kubernetes cluster.
Proposed change¶
The following changes are required in new MgmtDriver:
instantiate_end:
Execute Ansible playbook to create Kubernetes cluster.
Install and initialize Load Balancer.
scale_start, scale_end:
Execute Ansible playbook to join new Worker nodes.
Add/remove route to/from Load Balancer.
heal_start, heal_end (entire VNF):
Execute Ansible playbook to re-create Kubernetes cluster.
Re-install and re-initialize of Load Balancer.
heal_start, heal_end (target VNFC):
Execute Ansible playbook to re-create target nodes.
Add/remove route to/from Load Balancer.
Note
VNFC Heal operation with SOL002 is supported in the spec “Support Healing Kubernetes Master/Worker-nodes with Mgmtdriver” [4] but, in this spec, Heal operation for Master node is not supported because kubespray doesn’t provide a playbook for it.
Note
The sample MgmtDriver assumes to have pre-built Ansible server. MgmtDriver connects to Ansible server via SSH and runs playbooks with CLI assuming that Ansible command is executable. Also, sshpass should be installed.
VNFD for operation¶
The following part should be added to VNFD in the User document of “How to use Mgmt Driver for deploying Kubernetes Cluster” [7]:
VNFD (TOSCA):
substitution_mappings:
...
requirements:
virtual_link_external: [ externalLB_CP1, virtual_link ]
...
node_templates:
...
externalLB:
type: tosca.nodes.nfv.Vdu.Compute
...
externalLB_CP1:
type: tosca.nodes.nfv.VduCp
...
requirements:
- virtual_binding: externalLB
...
externalLB_CP2:
type: tosca.nodes.nfv.VduCp
...
requirements:
- virtual_binding: externalLB
- virtual_link: internalVL
...
Heat template (Base HOT):
heat_template_version: 2013-05-23
description: 'ExternalLB HOT for Sample VNF'
parameters:
flavor:
type: string
image:
type: string
public_network:
type: string
net1:
type: string
resources:
externalLB:
type: OS::Nova::Server
properties:
flavor: { get_param: flavor }
name: externalLB
image: { get_param: image }
networks:
- port:
get_resource: externalLB_CP1
- port:
get_resource: externalLB_CP2
externalLB_CP1:
type: OS::Neutron::Port
properties:
network: { get_param: public_network }
externalLB_CP2:
type: OS::Neutron::Port
properties:
network: { get_param: net1 }
Instantiate Kubernetes cluster VNF¶
This section describes how to create a Kubernetes cluster in MgmtDriver
instantiate_end() method with kubespray Ansible playbooks.
Design of operation¶
The following depicts the diagram of instantiate process of Kubernetes cluster:
+---------------+ +---------+
| ExternalLB | | |
| Script | | VNFD |
| | | |
+-------------+-+ +-+-------+
| |
v v +---------------+
+--+-----+-+ | Instantiation |
| | | Request with |
| CSAR | | Additional |
| | | Params |
+----+-----+ +-+-------------+
| |
| | 1. Send request
+-----------------------------------------+
| | | VNFM |
| v v |
| +----+----------+----+ |
| | TackerServer | |
| +-------+------------+ |
| | |
| +---------------------------------+ |
| | | Tacker Conductor | |
| | v | |
| | +--------+------------+ | |
| | | VnflcmDriver | | |
| | +------+-----------+--+ | |
| | | | | |
| | v v | |
| | +------+-----+ +--+--------+ | |
| | | Mgmt | | OpenStack | | |
+----------------+ Driver | | Infra | | |
| | | | | | Driver | | |
v | | +-----------++ +-------+---+ | |
+-----+------+ | | | | | |
| Ansible | | +---------------------------------+ |
| | | | | |
+-------+----+ +-----------------------------------------+
1. Install | | |
Kubernetes +------------+ 4. Install +------+ | 2. Create VMs
cluster | | ExternalLB | v
+----------------------------------------------+-----------+
| | | | VNF |
| v v v |
| +-------------+ +-------------+ +----------------+ |
| | +---------+ | | +---------+ | | +------------+ | |
| | | Worker | | | | Master | | | | ExternalLB | | |
| | +---------+ | | +---------+ | | +------------+ | |
| | VM | | VM | | VM | |
| +-------------+ +-------------+ +----------------+ |
+----------------------------------------------------------+
+----------------------------------------------------------+
| Hardware Resources |
+----------------------------------------------------------+
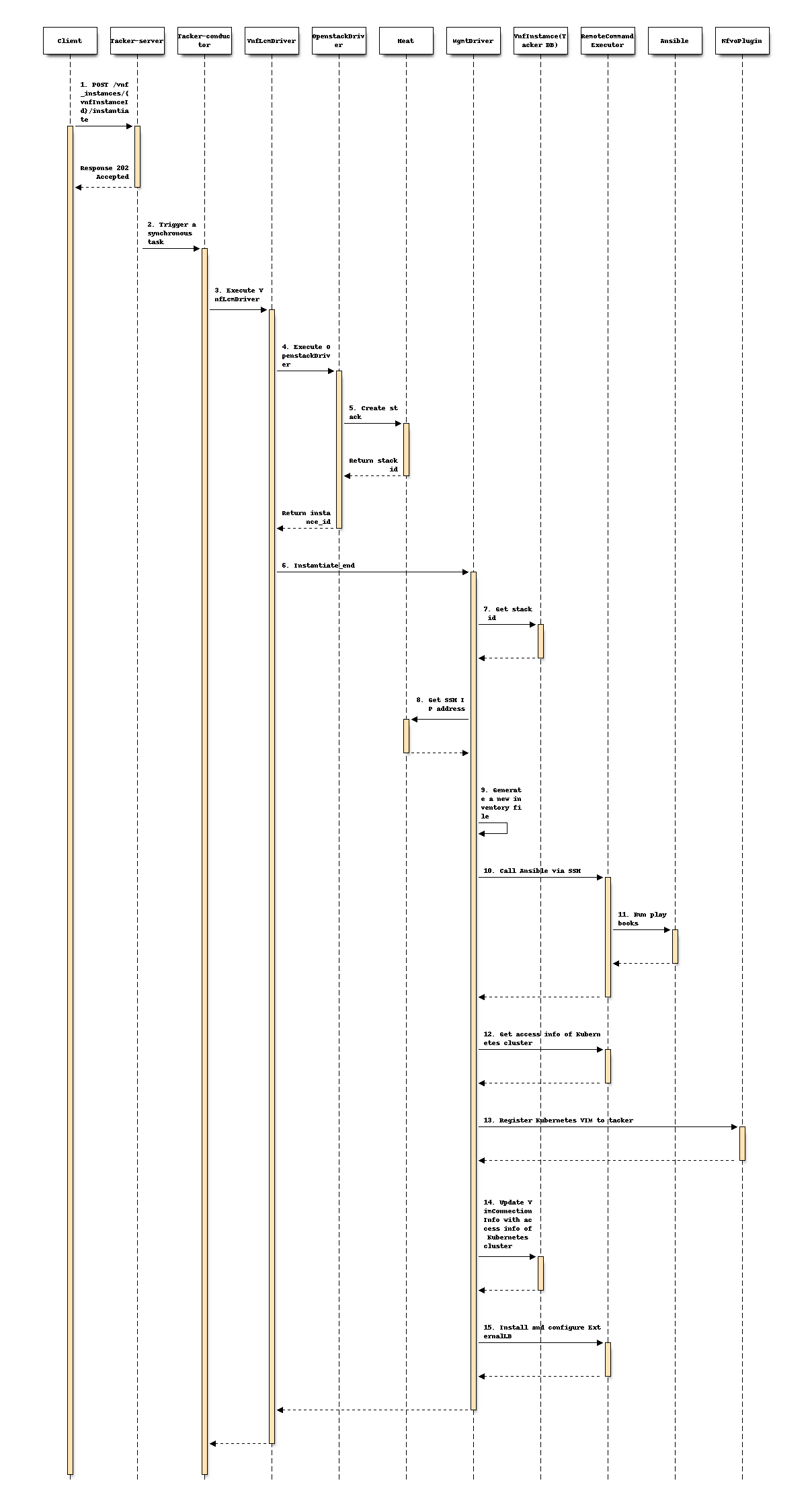
New steps are required in instantiate_end() method of MgmtDriver to
“VNF-A: Create VMs and set up Kubernetes cluster (Kube-adm)” chapter of
spec [2].
1-8. Existing process
9-11. Add the following process in instantiate_end to install Kubernetes cluster.
MgmtDriver generates an inventory file.
The inventory file includes all IP address of deployed Master and Worker nodes. The following is a sample of inventory file:
[all] node1 Ansible_host=95.54.0.12 ip=10.3.0.1 etcd_member_name=etcd1 Ansible_user=user1 Ansible_password=password1 node2 Ansible_host=95.54.0.13 ip=10.3.0.2 etcd_member_name=etcd2 Ansible_user=user2 Ansible_password=password2 node3 Ansible_host=95.54.0.14 ip=10.3.0.3 etcd_member_name=etcd3 Ansible_user=user3 Ansible_password=password3 node4 Ansible_host=95.54.0.15 ip=10.3.0.4 etcd_member_name=etcd4 Ansible_user=user4 Ansible_password=password4 node5 Ansible_host=95.54.0.16 ip=10.3.0.5 etcd_member_name=etcd5 Ansible_user=user5 Ansible_password=password5 node6 Ansible_host=95.54.0.17 ip=10.3.0.6 etcd_member_name=etcd6 Ansible_user=user6 Ansible_password=password6 [kube_control_plane] node1 node2 node3 [etcd] node1 node2 node3 [kube-node] node4 node5 node6 [calico-rr] [k8s-cluster:children] kube_control_plane kube-node calico-rrMgmtDriver calls kubespray Ansible playbooks named cluster.yml to install Kubernetes cluster.
Transfer inventory file to Ansible server via SCP or SFTP.
Access the Ansible server via SSH, and runs Ansible playbook named cluster.yml.
Sample command in Ansible server:
ansible-playbook -i inventory/mycluster/hosts.ini --become --become-user=root cluster.ymlAnsible installs Kubernetes on Master and Worker nodes, including kubeadm, kubelet, etcd cluster.
12-14. Existing process
Add the following process in
instantiate_endto install and configure External Load Balancer.Transfer a shell script files specified in script_path via SCP or SFTP.
Install External Load Balancer and set initial configuration with script files.
Note
TBD: Dedicated Ansible playbooks or shell scripts may be required for all steps to install and configure Kubernetes cluster.
Request parameters for operation¶
User gives the following instantiate parameter to
“POST /vnf_instances/{id}/instantiate” as
InstantiateVnfRequest data type in ETSI NFV-SOL003 v2.6.1 [5]:
Add the following attributes to additionalParams described in the
User document
“How to use Mgmt Driver for deploying Kubernetes cluster” [2].
additionalParams:
Attribute name
Cardinality
Parameter description
k8s_cluster_installation_param
1
Configuration for Kubernetes cluster installation.
>ansible
0..1
Structure. Specify Ansible related configuration such as ip address (
ip_address) and playbook (kubespray_root_path) to execute.>>ip_address
1
String. IP address of Ansible server.
>>username
1
String. Username of Ansible server.
>>password
1
String. Password of Ansible server.
>>kubespray_root_path
1
String. Root directory of kubespray.
>>transferring_inventory_path
1
String. Target path to transfer the generated inventory file.
>external_lb_param
0..1
Structure. Properties to install External Load Balancer.
>>ssh_cp_name
1
String. Resource name of CP to access to deployed VM via SSH.
>>ssh_username
1
String. User name of deployed VM to access via SSH.
>>ssh_password
1
String. Password of deployed VM to access via SSH.
>>script_path
1
String. Path of the installation shell script for External Load Balancer.
Note
SSH access with public key authentication is not supported.
The following is a sample of request body:
{
"flavourId": "simple",
"additionalParams": {
"k8s_cluster_installation_param": {
"script_path": "",
"vim_name": "kubernetes_vim",
"ansible": {
"ip_address": "0.0.0.0",
"username": "ansible",
"password": "ansible",
"kubespray_root_path": "",
"transferring_inventory_path": ""
},
"master_node": {
"aspect_id": "master_instance",
"ssh_cp_name": "masterNode_CP1",
"nic_cp_name": "masterNode_CP1",
"username": "ubuntu",
"password": "ubuntu",
"pod_cidr": "192.168.3.0/16",
"cluster_cidr": "10.199.187.0/24",
"cluster_cp_name": "masterNode_CP1"
},
"worker_node": {
"aspect_id": "worker_instance",
"ssh_cp_name": "workerNode_CP2",
"nic_cp_name": "workerNode_CP2",
"username": "ubuntu",
"password": "ubuntu"
},
"proxy": {
"http_proxy": "http://user1:password1@host1:port1",
"https_proxy": "https://user2:password2@host2:port2",
"no_proxy": "192.168.246.0/24,10.0.0.1",
"k8s_node_cidr": "10.10.0.0/24"
},
"external_lb_param": {
"ssh_cp_name": "externalLB_instance",
"ssh_username": "ubuntu",
"ssh_password": "ubuntu",
"script_path": "./Scripts/ExternalLB_installation.sh"
}
},
"lcm-operation-user-data": "./UserData/k8s_cluster_user_data.py",
"lcm-operation-user-data-class": "KubernetesClusterUserData"
},
"extVirtualLinks": [
{
"id": "net0_master",
"resourceId": "b0b84da3-3259-4855-b4cd-5711ba5e5de1",
"extCps": [
{
"cpdId": "masterNode_CP1",
"cpConfig": [
{
"cpProtocolData": [
{
"layerProtocol": "IP_OVER_ETHERNET"
}
]
}
]
}
]
},
{
"id": "net0_worker",
"resourceId": "b0b84da3-3259-4855-b4cd-5711ba5e5de1",
"extCps": [
{
"cpdId": "workerNode_CP2",
"cpConfig": [
{
"cpProtocolData": [
{
"layerProtocol": "IP_OVER_ETHERNET"
}
]
}
]
}
]
},
{
"id": "net0_externalLB",
"resourceId": "b0b84da3-3259-4855-b4cd-5711ba5e5de1",
"extCps": [
{
"cpdId": "externalLB_CP1",
"cpConfig": [
{
"cpProtocolData": [
{
"layerProtocol": "IP_OVER_ETHERNET"
}
]
}
]
}
]
}
],
"vimConnectionInfo": [
{
"id": "3cc2c4ff-525c-48b4-94c9-29247223322f",
"vimId": "05ef7ca5-7e32-4a6b-a03d-52f811f04496",
"vimType": "openstack"
}
]
}
Scale-out/in Worker nodes of Kubernetes cluster VNF¶
This section describes how to Scale-out/in Worker nodes with Ansible interface in MgmtDriver and with Load Balancer. In Scale-out operation, new Worker nodes requires Kubernetes related package installation with kubespray playbooks, and Load Balancer needs to add the route for new Worker nodes.
Scale-out¶
The process is almost the same with “Scale-out” chapter of spec [3],
except for the MgmtDriver part.
The scale_end operation in MgmtDriver needs the following new steps:
Update the inventory file to add new Worker nodes.
Call kubespray Ansible playbook.
Access the Ansible server via SSH.
Run Ansible playbook named scale.yml to install new Worker nodes.
Sample command in Ansible server:
ansible-playbook -i inventory/mycluster/hosts.ini --become --become-user=root scale.yml
Transfer a shell script specified by script_path provided in Instantiate operation via SCP or SFTP.
Update route configuration in Load Balancer with the script.
Scale-in¶
The process is almost the same with “Scale-in” chapter of spec [3],
except for the MgmtDriver part.
The scale_start operation in MgmtDriver needs the following new steps:
Transfer a shell script specified by script_path provided in Instantiate operation via SCP or SFTP.
Delete route from Load Balancer for Worker nodes planned to be deleted with the script.
Evacuate Pods from the Worker nodes planned to be deleted.
Access a Master node via SSH.
Execute evacuation command.
Sample command in Master node:
kubectl drain <Worker node to be deleted>
Call kubespray Ansible playbook.
Access the Ansible server via SSH.
Update the inventory file to delete Worker nodes.
Run Ansible playbook named remove-node.yml to delete target Worker nodes.
Sample command in Ansible server:
ansible-playbook -i inventory/mycluster/hosts.ini --become --become-user=root remove-node.yml -e node=<Worker node to be deleted>
Heal Master/Worker nodes in Kubernetes cluster VNF¶
In this spec, Heal operation for Master node with SOL002 is not supported. The following part describes how to heal a Kubernetes cluster VNF with SOL003 and how to heal Worker nodes in the Kubernetes cluster with SOL002.
Heal Kubernetes cluster¶
All required process in the Heal operation of entire Kubernetes cluster VNF
is already described in the spec
“Support deploying Kubernetes cluster with MgmtDriver” [2]
for heal_start and in Instantiate Kubernetes cluster VNF for heal_end.
heal_start operation is same as terminate_end, and
heal_end operation is same as instantiate_end.
Heal Worker nodes in Kubernetes cluster¶
The process is almost the same with “Healing a node in Kubernetes cluster with SOL002” chapter of the spec “Support Healing Kubernetes Master/Worker-nodes with Mgmtdriver” [4] except for the MgmtDriver part.
For new steps in MgmtDriver, heal_start is the same with scale_start
in Scale-in operation,
and heal_end is also same with scale_end in Scale-out operation.
The detailed steps are described in Scale-out/in Worker nodes of Kubernetes cluster VNF.
Alternatives¶
None
Data model impact¶
None
REST API impact¶
None
Security impact¶
Implementation proposals described in this spec include security impacts such as the use of sudo and elevated privileges when running Ansible playbooks.
Notifications impact¶
None
Other end user impact¶
None
Performance Impact¶
None
Other deployer impact¶
None
Developer impact¶
None
Implementation¶
Assignee(s)¶
- Primary assignee:
Masaki Ueno <masaki.ueno.up@hco.ntt.co.jp>
- Other contributors:
Yoshito Ito <yoshito.itou.dr@hco.ntt.co.jp>
Kyosuke Hori <hori-kyosuke@fujitsu.com>
Yoshiyuki Katada <katada.yoshiyuk@fujitsu.com>
Ayumu Ueha <ueha.ayumu@fujitsu.com>
Liang Lu <lu.liang@fujitsu.com>
Work Items¶
MgmtDriver will be modified to implement:
Execute Ansible playbook.
Generate inventory files.
Provide a sample script to perform the following tasks:
Install and initialize of Load Balancer.
Add/remove route to/from Load Balancer.
Re-install and re-initialize of Load Balancer.
Add new unit and functional tests.
Dependencies¶
LCM operations for the Kubernetes cluster depend on the following specifications:
Instantiate operation for the Kubernetes cluster
Depends on spec “Support deploying Kubernetes cluster with MgmtDriver” [2].
Scale operation for the Kubernetes cluster
Depends on spec “Support scaling Kubernetes Worker-nodes with Mgmtdriver” [3].
Heal operation for the Kubernetes cluster
Depends on spec “Support Healing Kubernetes Master/Worker-nodes with Mgmtdriver” [4].
Testing
Unit and functional tests will be added to cover cases required in the spec.
Documentation Impact¶
As for Lifecycle Management of Kubernetes cluster, complete user guide will be added to explain the following two steps:
How to use kubespray Ansible playbook.
How to set up External Load Balancer.
